
If your hours of work change from week-to-week, your employer must: You may also find your hours in an Employment Regulation Order or Registered Employment Agreement.

Usually, you can find your working hours and work patterns in your contract of employment. You can read more about young people’s working hours.
If you are under 18, there are different maximum working hours, breaks and rules on night work. You can read more about night workers and minimum breaks and rest periods. Employees in certain categories of civil protection services.Family employees on farms or in private homes.Employees who control their own working hours.The law on working time and rest periods does not apply to all employees. There are also special conditions for employees who work on Sundays – see 'Sunday working and overtime' below.įor most employees, the law on working time and breaks is set out in the Organisation of Working Time Act 1997 - see 'the laws on work hours' below. The 48 hours of work do not include time spent on annual leave, sick leave, maternity leave, adoptive leave or parental leave. If you are under 18, there are different rules (see below). A working week can be more than 48 hours, it is the average that is important. Common Usage: Typical users of the shift configuration.The maximum number of hours you can work in an average working week is 48 hours.Minuses: Negative aspects of the shift configuration.Pluses: Positive aspects of the shift configuration.Note that by default, each team contains the same number of employees. A shift configuration is "balanced from day to day" if each day is staffed by the same number of employees. A shift configration is "balanced from shift to shift" if the new shift will be staffed by the same number of employees as the old shift. Staffing Fluctuation: The fluctuation in staffing level as the plan progresses from shift to shift and day to day.Average Hours Per Week: This is the average number of hours worked by each employee per week based on the shift lengths and shift sequences for this plan.In a "slow" rotation, a team works the same shift for many days or weeks before rotating to another shift. In a "fast" rotation, a team rotates from one shift to another once every few days or less. The rotation speed is the speed at which the shifts are rotated. Many studies suggest that forward rotation is better than backward rotation since our body adjusts much better to changes in work shifts from earlier to later. In a backward rotation, the reverse is true. In a forward rotation, the team rotates from a shift that starts earlier in the day to a shift that starts later in the day, e.g. Rotation: For rotating shift configurations, a team rotates from one shift to another according to a specific arrangement.At the end of each repeat cycle, the team starts the same shift sequence over again. Repeat Cycle: The number of days required for each team to complete its assigned shift sequence in a schedule plan.The shift start or end time can be adjusted to fit your business operations so long as the shift length stays the same. For each shift, only the shift description and shift length are shown.
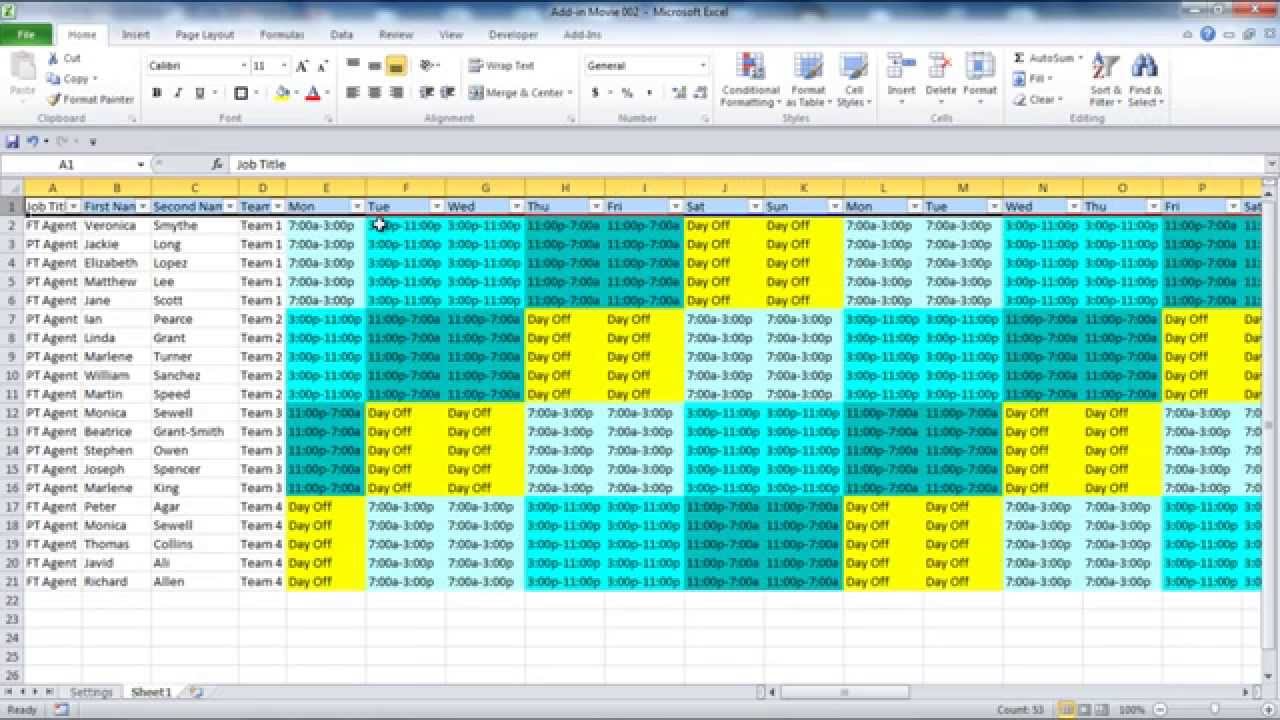
Shifts: The different shifts used in this shift pattern.

A team may consist of one or more employees.
#4 10 work schedule code#
Plan ID: A code used to uniquely identify the shift plan in Snap Schedule employee scheduling software.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
